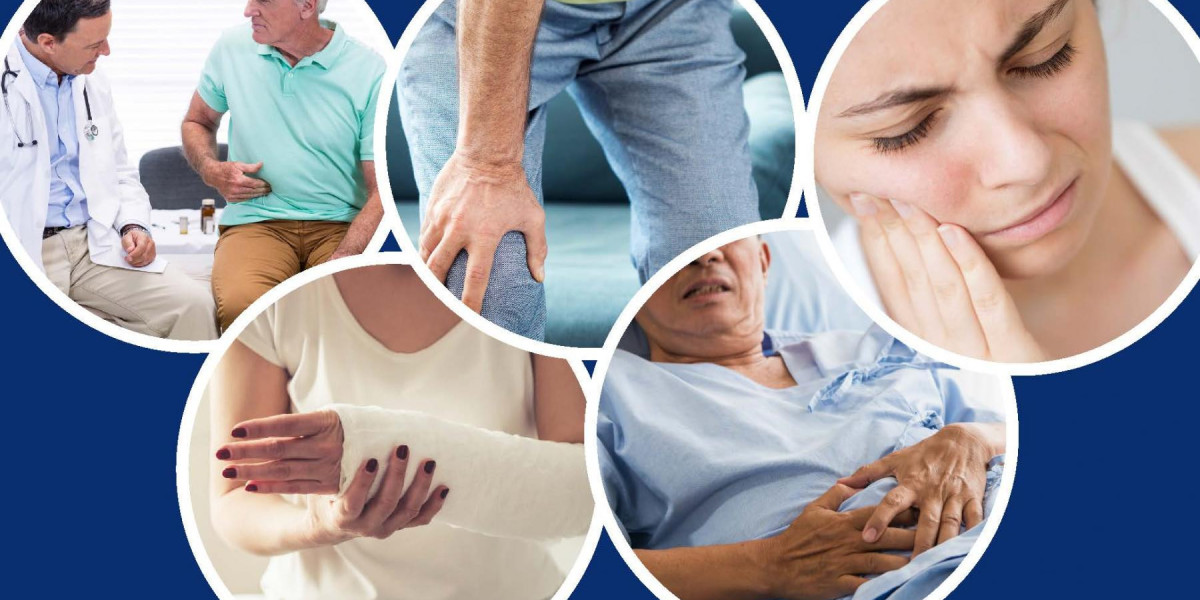
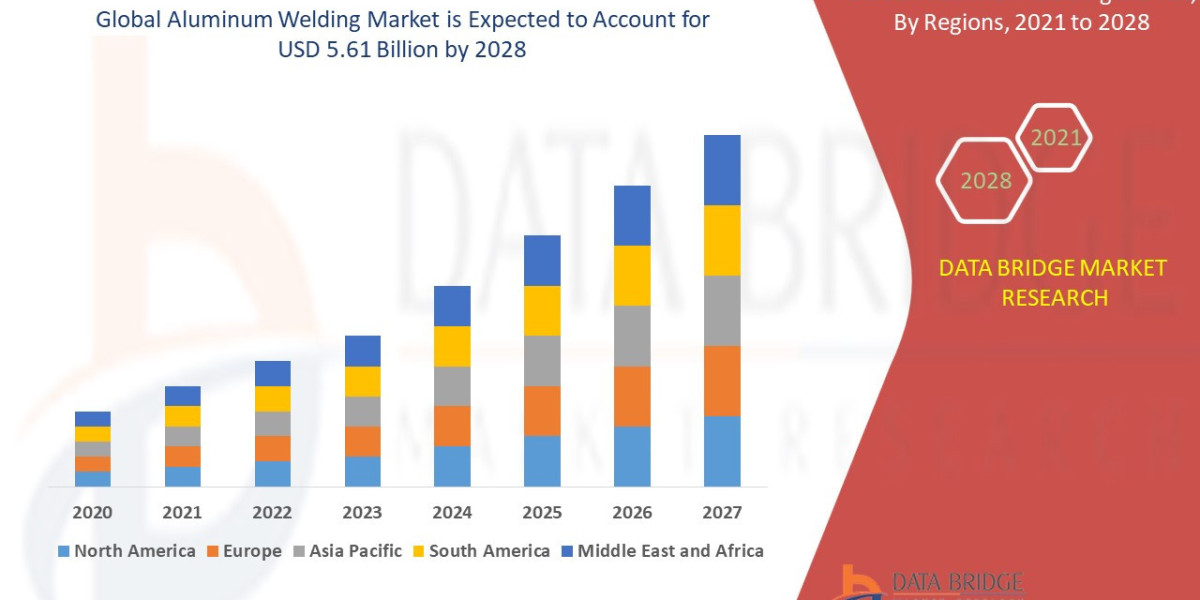
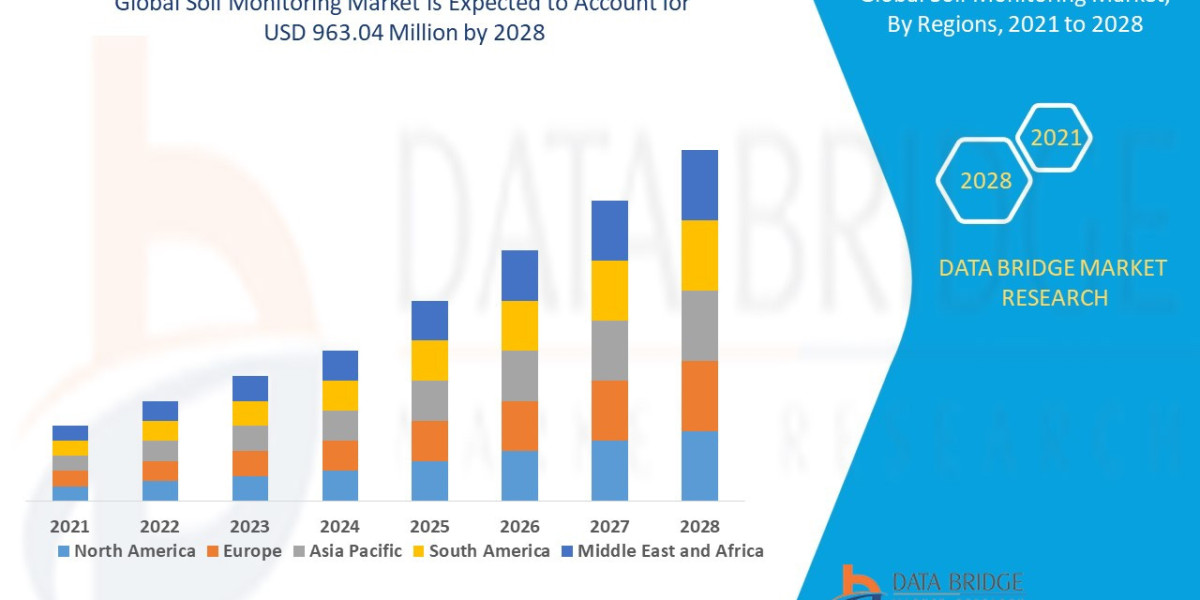
Acute pain is a common and often debilitating condition that can arise from various sources, impacting individuals’ daily lives significantly. Whether it's due to an injury, surgical procedure, or medical illness, acute pain serves as a vital warning signal that something is wrong in the body. Seeking help from professionals, such as those at a NYC Psychiatrist Addiction Clinic, can provide essential support for patients dealing with pain and its psychological impacts. This blog will explore the nature of acute pain, its causes, treatment options, and effective management strategies.
What Is Acute Pain?
Acute pain is defined as sudden pain that typically lasts for a short duration, often less than three to six months. This type of pain is usually a direct result of tissue damage or injury. It can manifest in various forms, including sharp, throbbing, or aching sensations. Unlike chronic pain, which persists over time, acute pain usually resolves as the underlying condition heals.
Causes of Acute Pain
Acute pain can stem from numerous causes, including:
Injuries: Sprains, fractures, and other physical injuries often result in acute pain. The body’s response to injury includes inflammation and pain, signaling the need for care.
Surgical Procedures: Post-operative pain is a common experience for individuals who have undergone surgery. This pain is typically temporary and subsides as the healing progresses.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as appendicitis or pancreatitis, can trigger acute pain. These conditions may require immediate medical attention to address the underlying issue.
Infections: Infections can cause localized pain, such as in the case of an abscess or systemic pain, as seen in conditions like pneumonia.
Understanding the specific cause of acute pain is crucial for effective treatment and recovery.
Treatment Options for Acute Pain
The treatment of acute pain often depends on its cause and severity. Here are some common approaches:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are often the first line of defense. In some cases, stronger medications like opioids may be prescribed for more severe pain. It’s essential to use these medications under medical supervision, especially when considering options like where to buy Tramadol online, as misuse can lead to dependency.
Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help alleviate pain and improve mobility. Therapists may use techniques such as exercise, massage, and stretching to aid recovery.
Rest and Ice: In many cases, resting the affected area and applying ice can help reduce swelling and pain. This is particularly effective for injuries.
Injections: For severe pain, corticosteroid injections or nerve blocks may be utilized to provide relief.
Surgery: In some instances, surgery may be necessary to address the underlying cause of pain, especially if it is due to structural problems.
Psychological Impact of Acute Pain
Acute pain can have significant psychological effects, including anxiety and depression. The stress of experiencing pain can lead to a cycle of fear and avoidance, potentially causing individuals to limit their activities. This is where the support of a mental health professional, such as those at a NYC Psychiatrist Addiction Clinic, can be invaluable. They can help patients develop coping strategies and address any psychological issues that may arise from their pain experience.
Managing Acute Pain at Home
In addition to professional treatment, individuals can take steps at home to manage acute pain effectively:
Stay Informed: Understanding your condition and treatment options can empower you to make informed decisions about your care.
Practice Relaxation Techniques: Methods such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and alleviate pain.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep can support overall health and aid recovery.
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals. Rest when needed, but also engage in light activity as tolerated to promote healing.
Conclusion
Acute pain is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective treatment and management. Understanding its causes, exploring treatment options, and addressing the psychological aspects are crucial for recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with acute pain, consider reaching out to medical professionals for guidance. Utilizing resources such as a NYC Psychiatrist Addiction Clinic can provide essential support in navigating the challenges of pain and ensuring a comprehensive treatment plan.